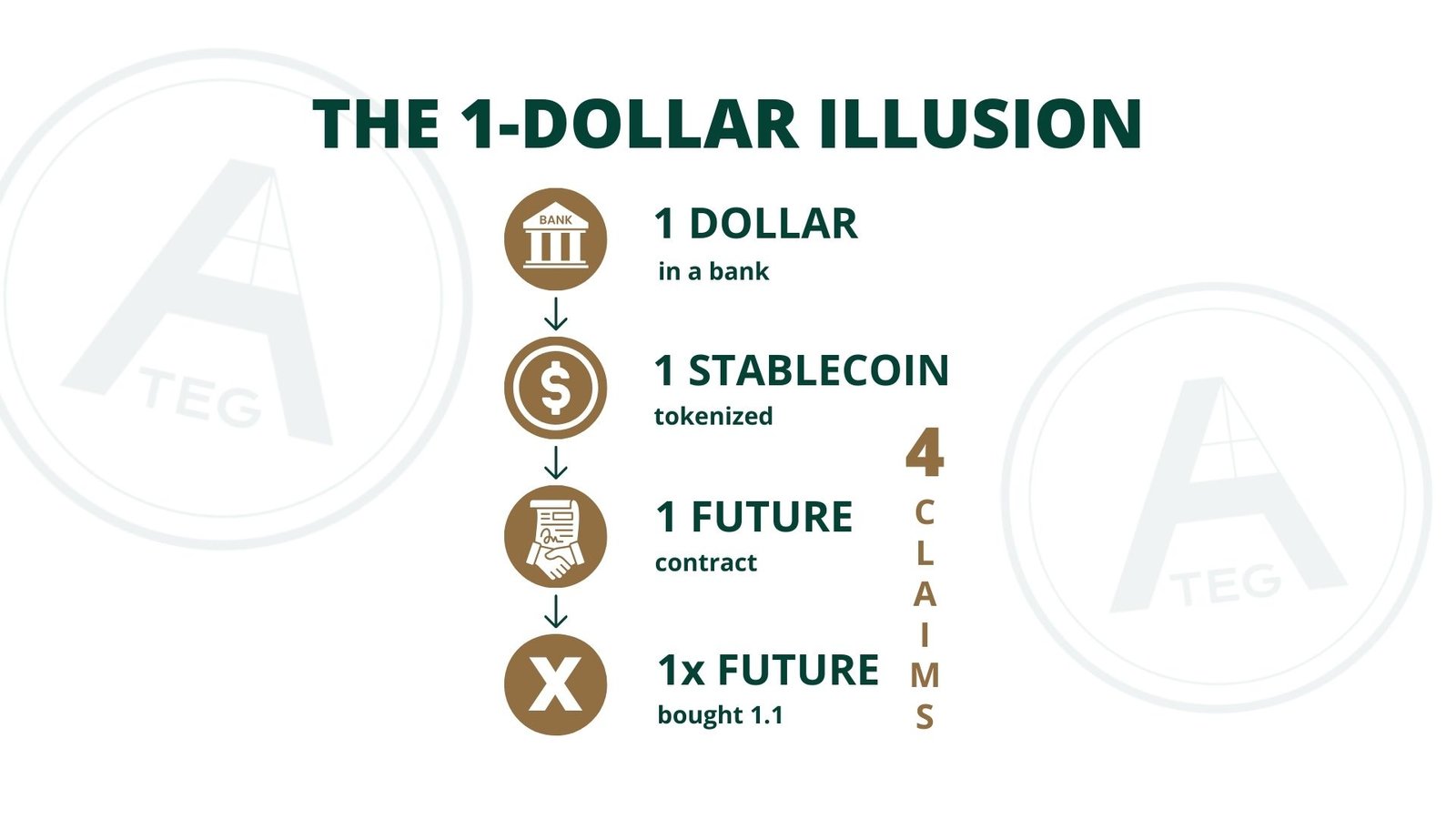
1️⃣ The Original Dollar: A Bank Deposit
The process begins with a single physical dollar deposited into a bank account. This deposit becomes part of the bank’s reserves. While the customer sees the full amount on their account balance, the bank simultaneously uses a portion of that money to issue loans or invest in financial instruments.
This is the foundation of fractional-reserve banking.
✔️ Claim #1:
The bank balance — the customer believes they still own that dollar.
2️⃣ The Tokenized Dollar: A Stablecoin
Stablecoin issuers, whether regulated or not, often follow a straightforward model: a dollar deposited into their reserve account results in the creation of one digital token, usually pegged 1:1 to USD.
This token can circulate globally, be traded, lent, borrowed, or used in DeFi. Yet the underlying collateral is still the same single dollar sitting in a bank.
✔️ Claim #2:
The stablecoin — a digital representation of the same dollar.
3️⃣ The Derivative Dollar: Using the Stablecoin as Collateral
Once a stablecoin exists, it can be deposited into exchanges or decentralized platforms and used as collateral for loans, margin positions, or synthetic assets. Traders can open leveraged positions or mint additional digital assets based on this collateral.
A new financial instrument is created, backed indirectly by the original bank dollar.
✔️ Claim #3:
The credit or derivative created using the stablecoin as collateral.
4️⃣ The Leveraged Dollar: Futures and Perpetual Contracts
Taking it one step further, the derivative itself can be used to open futures contracts or perpetual swap positions. These instruments represent synthetic exposure to an asset, without any underlying transfer of real value. Yet each position reflects capital that appears to be “backed.”
This fourth layer is purely a financial claim, but it behaves on markets as if it were real money.
✔️ Claim #4:
The leveraged future or perpetual position.
🧩 A Simple Example: One Dollar, Four Paths
To understand the process more clearly, consider the following neutral illustration:
- A person deposits 1 real dollar into a bank.
- A stablecoin issuer mints 1 digital dollar (stablecoin) backed by that deposit.
- A trader uses that stablecoin to purchase $1 worth of Bitcoin on a spot market.
- A different trader uses that Bitcoin exposure to open a $1 Bitcoin futures position, creating a synthetic claim.
In this scenario:
- One trader may profit on the Bitcoin position.
- Another may profit or lose on the futures position.
- The stablecoin continues circulating.
- The original bank dollar never moved.
💴 One Dollar, Four Claims
At this stage, the financial system has produced four separate claims:
- The bank deposit
- The stablecoin
- The derivative or loan
- The leveraged synthetic position
All four exist simultaneously.
All four behave like capital.
But all four originate from the same single dollar.
No fraud is involved.
No illegal behavior.
This is simply how modern financial and digital markets function.
👁️ Why Most People Never Notice
The complexity of these systems creates a form of “financial illusion.”
People see the balance in their bank, the stablecoin in their wallet, the open position in their trading account, or the yield from a DeFi platform—but they rarely understand that these are layered representations of the same foundational value.
This structural illusion explains:
- how liquidity can exceed real money supply
- why markets can destabilize quickly
- why shocks spread across both crypto and traditional finance
- why transparency matters more than ever
Understanding this is not just knowledge—it is a form of empowerment.
🌍 Why This Matters for the Future of Crypto and Real-World Assets
The multiplication of claims becomes risky when no real economic activity stands behind the system. When financial value is created faster than real value, markets become dependent on sentiment, leverage, and liquidity cycles rather than fundamentals.
This is one reason why the industry is shifting toward models backed by:
- real cashflows
- real assets
- real economic productivity
Digital assets backed by genuine economic activity create grounding. They connect the financial layer to the real world instead of multiplying claims on the same unit of value.
🧠 A New Era Requires a New Understanding
The goal of this article is to help readers see what is often invisible.
The mechanics behind stablecoins, derivatives, and synthetic markets are not inherently negative — but they only become sustainable when paired with systems that generate real value.
Understanding how one dollar becomes four financial claims is the first step toward recognizing why the market needs models built on transparency, substance, and measurable economic foundations.